Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Human Computer Interaction in Everyday Life by Using Deep Learning
Authors: Prof. Ritesh Deshmukh, Gayatri Gadekar, Sujal Ghayal, Sakshi Khandare, Rohit Kolse, Mayuri Jadhao, Sakshi Thorat
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.61551
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Human Computer Interaction (HCI) is the design and implementation of interactive computing systems that users can interact with. It includes desktop systems in different devices. Success of a technology simply results from the easiness with which the user can interact with it [2]. A simple and easy way to use a system doesn\'t mean that a simple technology is behind such a system. The most important concepts in HCI are functionality and usability. Usability is when a user utilizes the system\'s functions easily, properly and clearly. Functionality and usability may vary from one system to another. In this project we interact with computer by using deep learning. HCI spread through various everyday human activities, transforming the way we communicate, learn and entertain ourselves. With the help of this project we explores the impact of smartphones, tablets and wearable devices on personal productivity and communication.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is about making computer stuff easy for people. It's about designing computer screens and gadgets so that they're simple to use and understand. HCI experts make sure these things work well for people in everyday life. They think about how people use computers and how it affects them. They use what we know about how our brains work with computers to make things better. They also make sure that the things on our screens look good and are easy to read. So, HCI is all about making computers and people work together nicely[2].In HCI, people are really important. They're the ones who use computers and technology by typing on keyboards, tapping on touchscreens, or speaking commands. People give feedback about how easy or difficult it is to use technology, which helps make it better. They also learn how to use new technology and choose what software or settings they like best. Some people even create things or change how their computer looks. HCI is all about understanding what people want and need when they use technology, and making sure it works well for them. The computer is like the main connector in HCI. It helps humans interact with the digital world[1]. How the computer looks, what it can do, and how well it works all affect how people use it. HCI experts work hard to make sure computers are easy to use, work well for people, and meet their needs. They want technology to be user-friendly and match what people expect. HCI is also about studying how people use computers and making them easier to use. It looks at things like how we interact with computers and what the screens and buttons look like.
A. Human
In Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), people are really important. They're the ones who use computers and technology. They do this by typing on keyboards, tapping on touchscreens, or speaking commands. People give feedback about how easy or difficult it is to use technology, which helps make it better. They also learn how to use new technology and choose what software or settings they like best. Some people even create things or change how their computer looks. [3] HCI is all about understanding what people want and need when they use technology, and making sure it works well for them.
B. Computer
In Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), the computer is like the main connector. It helps humans interact with the digital world. How the computer looks, what it can do, and how well it works all affect how people use it. HCI experts work hard to make sure computers are easy to use, work well for people, and meet their needs. They want technology to be user-friendly and match what people expect.
C. Interaction
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is about studying how people use computers and making them easier to use. It looks at things like how we interact with computers and what the screens and buttons look like.
II. PURPOSE OF THE PROJECT
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is like a bridge connecting people and computers, making it easier for us to use technology.[4] Think of your hand as an example of HCI: each finger represents something important. One finger makes sure using computers is easy, another makes it enjoyable, and another ensures everyone can use them, no matter their abilities. Another finger helps us do things faster and more easily, and the last one makes sure technology respects our rights and values.[5] Just like each finger has a job, HCI aims to combine these things to make technology that's easy, inclusive, fast, customizable, and fair, making our interactions with computers better every day.
III. OBJECTIVE
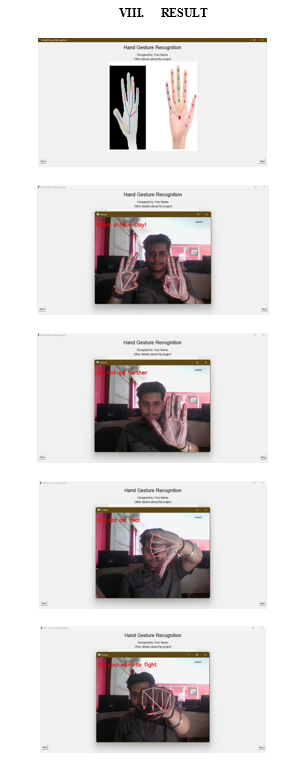
The goal of this subject is to learn how to make technology that's easy for people to use. We'll learn how to design and test systems that people can interact with, how to make designs faster using models of how people think, and some rules for designing technology that's easy to use. For our project, we'll use Python to create a system where we can interact with a computer using gestures and signs. [8] For example, if we wave hello to the computer, it will show a message on the screen saying hello back. This project can also be helpful for people with disabilities. For instance, if someone who can't speak wants to send a message, they can do it using gestures, and the computer will respond immediately.
IV. LITERATURE REVIEW
The field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) indeed encompasses a range of perspectives, which has led to discussions about whether it is a science, a design science, or an engineering discipline.
Let's break down these perspectives:
A. HCI as a Science
This viewpoint emphasizes understanding human behavior, cognition, and interaction with computers through empirical observation, experimentation, and the development of theories. Newell & Card (1985) [8] all into this category, suggesting that HCI involves scientific inquiry into how humans and computers interact. This perspective seeks to uncover general principles and laws governing human-computer interaction.
B. HCI as a Design Science
Carroll & Campbell (1989) [12] advocate for viewing HCI as a design science, focusing on the creation and evaluation of artifacts (i.e., computing systems) that support human activities. This perspective emphasizes the iterative process of design, evaluation, and refinement, drawing upon both scientific knowledge and practical design principles.[10] It involves crafting solutions to real-world problems and developing methodologies for creating usable and effective computing systems.
C. HCI as an Engineering Discipline
Another perspective sees HCI as an engineering discipline, concerned with the application of scientific principles and design methods to build reliable and efficient computing systems that meet human needs. This viewpoint emphasizes the systematic approach to designing, implementing, and evaluating interactive systems, often with a focus on scalability, reliability, and efficiency.[7] Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is about making sure that people and computers work well together.[9] It involves designing, testing, and building computer systems that are easy and useful for people to use. HCI looks at how humans interact with computers and how computers can be designed to fit human needs and tasks.[13] It's like creating bridges between people and machines. Unlike human factors, which focuses on designing for physical comfort and safety, HCI focuses more on designing interfaces for computers and making sure they work smoothly. When designing devices, it's important to think about how people think and behave when using them, because often people's abilities and the capabilities of devices don't match up perfectly.
V. METHODOLOGY
HCI is a field that brings together ideas from different areas to understand how people and computers interact. One important approach is user-centered design, where we involve users from the start to make technology that fits their needs.[11] We use various methods to do this, like watching how people use technology in real life, talking to them about what they want, and testing early versions of products with them. These methods help us make technology that's easy and useful for everyone.
A. User Research
User research techniques help us understand how people use technology better. Researchers study what people do and say to learn about their experiences.[4] They look for patterns and use different ways to collect information, like asking questions or watching people use technology. Instead of just looking at numbers, they focus on understanding how people feel and what they think about using technology.
VI. TECHNOLOGY
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs): GUIs are like the face of your computer or phone. They use pictures, buttons, and menus to help you do things easily.[8] Instead of typing a lot, you can just click on pictures or buttons to make your device work.
- Touchscreen Technology: Touchscreens on smartphones and tablets let you do things by tapping, swiping, and pinching your fingers. This makes using them easier and more fun. A touch screen digitizer is a special glass layer on your device that changes your finger's touch into signals it can understand.
- Voice Recognition: Voice recognition technology, like Siri and Alexa, lets you talk to your computer and devices instead of typing. It's like having a conversation with your devices, which makes using them simpler.
- Gesture Recognition: Gesture-based interaction, seen in devices like Microsoft Kinect or VR controllers, lets you control digital stuff using your body movements and gestures.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies make your computer interactions feel more immersive. AR lets you see digital stuff on top of the real world, while VR puts you in a whole virtual world.
- Haptic Feedback: Haptic technology makes you feel things through touch. For example, when you play games, your controller can vibrate or push back a bit, so you can feel what's happening in the game.
- Eye-Tracking: Eye-tracking technology lets computers know where you're looking, so they can do things based on that. This is useful in games and tools for people with special needs.
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint and facial recognition are ways to make sure only you can access certain things on your phone or computer. They're easy to use and very secure.
- Machine Learning and AI: AI-powered systems like chatbots and recommendation tools make your computer interactions more personal. Machine learning helps computers learn and get better at what they do over time.
- Accessibility Tools: Assistive technologies, like screen readers and special input devices, help people with disabilities use computers more easily.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP technologies help computers understand and talk back to us like humans do. They make chatting with computers possible.
VII. MODEL
A. Norman's Model of Interaction Explains how People use Technology in simple Steps[14]
- Deciding what you want to do: Think about what you want to achieve with the technology.
- Planning how to do it: Make a plan for how to accomplish your goal.
- Taking the action: Actually do what you planned.
- Carrying out the plan: Put your plan into action and do what you intended.
- Seeing what happens after your action: Observe what's happening around you after you've done something.
- Understanding what you see: Try to understand what's going on.
- Deciding if your goal was met: Finally, decide if you achieved what you wanted or if you need to adjust your plans.
B. The Interaction Model
Abowd and Beale compare using a computer to translating between different languages, breaking it down into four parts:
- User: This is what you want to do or tell the computer.
- Input: It's how you tell the computer what you want, like typing or clicking.
- System: This is what the computer does with your request, like processing it or running a program.
- Output: It's how the computer responds to what you asked or did, like showing information on the screen or making sounds.
Conclusion
HCI is becoming more important as more people use computers. The Internet and online shopping have made us think about how easy it is to use websites. By focusing on making technology easy to use, available to everyone, and following ethical rules, we can create a future where technology makes life better for everyone and helps people interact with computers in important and meaningful ways.
References
[1] Dix, A., Roselli, T., &Sutinen, E. (2006). E-learningand human-computer interaction: Exploring design synergies for more effective learning experiences. [2] Educational Technology & Society, 9(4), 1- [3] Fetaji, B., &Fetaji, M. (2007, September). E-learning indicators approach to developing e-learning software solutions. In EUROCON, 2007. The International Conference on &# 34; Computer as a Tool&# 34; (pp. 2687-2694). IEEE. [4] Thuseethan, S.Department Management System for Departments of Sri Lankan Universities. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 3(6). [5] Preece, J., Rogers, Y., Sharp, H., Benyon, D., Holland, S., & Carey, T. (1994).Human-computer interaction. Addison-Wesley Longman Ltd. [6] Danino, N. (2001). Human-Computer interaction and your site. November 14th. [7] Sivarajah, K., Achchuthan, S., & Umanakenan, R. (2014). Pay satisfaction and [8] Card, S. K., Moran, T. P., & Newell, A. (1983). The psychology of human-computer interaction. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. [9] Norman, D. A. (1988). The psychology of everyday things. Basic books. [10] Nielsen, J. (1993). Usability engineering. Morgan Kaufmann. [11] Shneiderman, B. (1992). Designing the user interface: strategies for effective human-computer interaction. Addison Wesley. [12] Carroll, J. M. (Ed.). (2003). HCI models, theories, and frameworks: Toward a multidisciplinary science. Morgan Kaufmann. [13] Dix, A., Finlay, J., Abowd, G., & Beale, R. (2004). Human-computer interaction. Prentice Hall. [14] Norman, D. A. (2002). The design of everyday things. Basic Books. [15] Dix, A., Finlay, J., Abowd, G., & Beale, R. (1998). Human-computer interaction (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall. [16] Preece, J., Rogers, Y., & Sharp, H. (2015). Interaction design: Beyond human-computer interaction.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Prof. Ritesh Deshmukh, Gayatri Gadekar, Sujal Ghayal, Sakshi Khandare, Rohit Kolse, Mayuri Jadhao, Sakshi Thorat. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET61551
Publish Date : 2024-05-03
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

